
Remember that if you are redirecting HTTP requests to the HTTPS port, you must use destination port 443 instead of 80. In the “Connection -> SSH -> Tunnels” section, add a new forwarded port by introducing the following values: Once you have your SSH client correctly configured and you have confirmed that you can successfully access your instance using SSH, you need to create an SSH tunnel in order to access phpMyAdmin.

PHPMYADMIN PASSWORD FREE
In the instructions below we have selected PuTTY, a free SSH client for Windows and UNIX platforms. In order to access phpMyAdmin via SSH tunnel, you need an SSH client.
PHPMYADMIN PASSWORD HOW TO
TIP: Refer to these instructions to learn how to obtain your private key. Watch the following video to learn how to easily access phpMyAdmin on Windows through an SSH tunnel: In this case, modify the steps below to use ports 81 or 443 respectively instead of port 80 for the tunnel endpoint. Similarly, if you have enabled Varnish (TM) or HTTPS redirection, your stack’s Web server might be accessible on port 81 (Varnish (TM)) or port 443 (SSL). If this port is already in use by another application on your local machine, replace it with any other port number greater than 1024 and modify the steps below accordingly. NOTE: The steps below suggest using port 8888 for the SSH tunnel. IMPORTANT: Before following the steps below, ensure that your Web and database servers are running. This implies that you must be able to connect to your server over SSH in order to access these applications remotely. To access it from a remote system, you must create an SSH tunnel that routes requests to the Web server from 127.0.0.1. Modify the available memory for the virtual machineįor security reasons, phpMyAdmin is accessible only when using 127.0.0.1 as the hostname.Auto-configure a Let's Encrypt certificate.Connect to the virtual machine from another host.Configure the application's IP address or hostname.Learn about the Bitnami Configuration Tool.Configure third-party SMTP for outbound emails.
PHPMYADMIN PASSWORD PASSWORD
Modify the default login password for the virtual machine.Understand what data Bitnami collects from deployed Bitnami stacks.Learn about Bitnami PHP application modules deprecation.Understand the default directory structure.Learn about the SSH warning 'REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED'.Configure password-based SSH authentication.PhpMyAdmin will work for both MariaDB and MySQL.Frequently Asked Questions for Virtual Machines Read this article to find out how: Create New Users and Grant Privileges If you for some reason can not get the root user to login, you may need to create an extra database user.
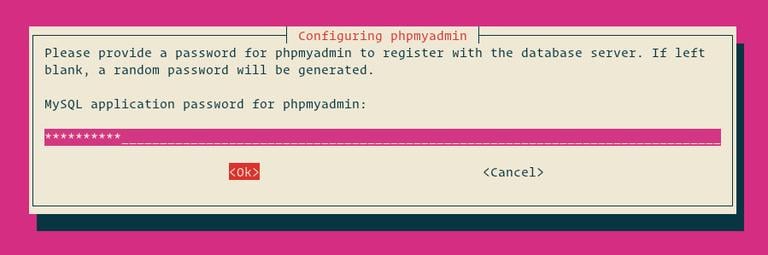
Of cause the expiration time can also be modified, but I think it is way cooler to make phpMyAdmin automatically login.Īlso note this must be added in the $cfg configuration array. The important parts to pay attention to here are the auth_type and of course user and password the default auth_type is cookie, but the annoying thing about this is that we need to login, and not least that it will expire in a short period of time, calling us to login yet again. Unfortunately, phpMyAdmin's default config file lacks a few options and comments explaining how to do this, but hopefully this article makes it more clear what to do. E.g: Some of the options may be present already, but likely commented out.
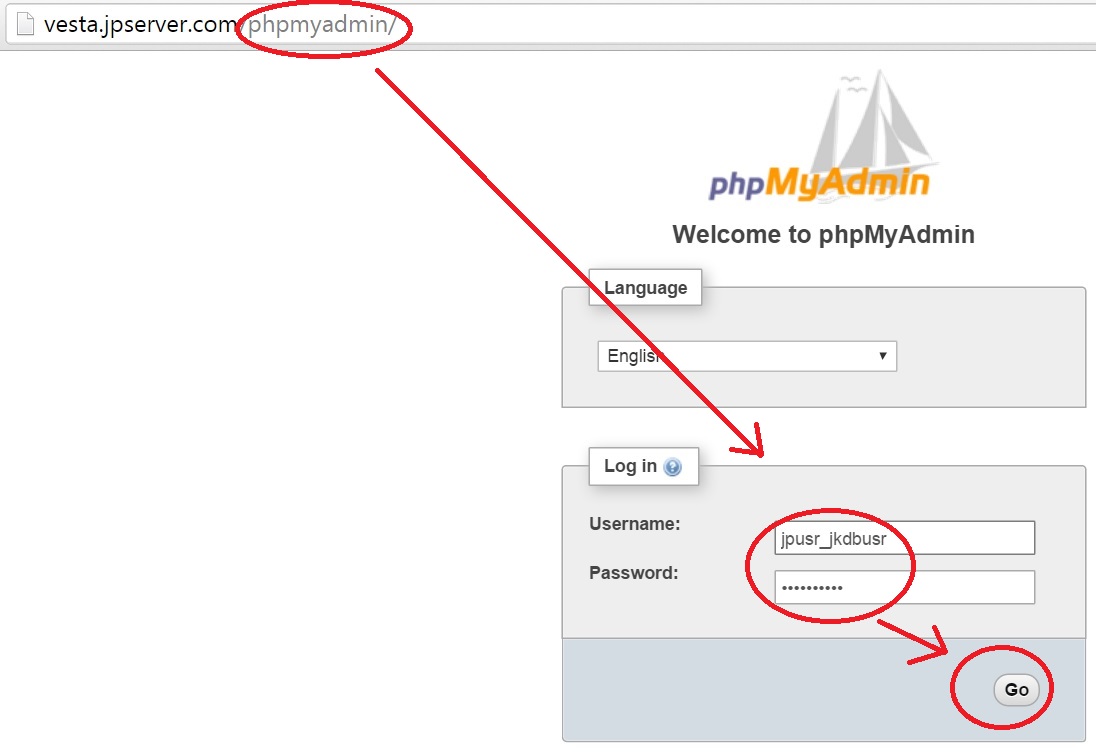
The configuration should become active immediately when you reload your browser window. * Authentication type */ $cfg = 'config' /* Server parameters */ $cfg = 'localhost' $cfg = false $cfg = false $cfg = 'root' $cfg = ''


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
